JIANGSU TIANCHENG GROUP LIMITED
Yaoguan Town, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province,China
+86-519-88387662
+86-519-85121683
steel_tube
steeltube.china
Tiancheng_Group
josen_dong
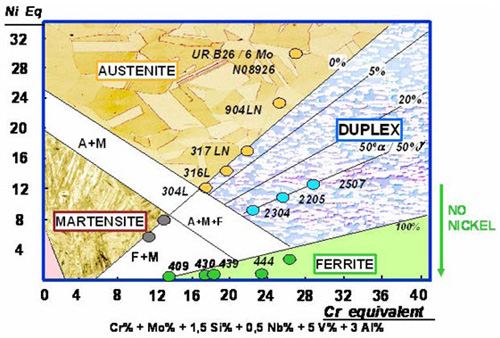
For these stainless steels; We can say that it definitely lives up to its name.
Duplex, as the name suggests, can be used as a double-sided material. Because it carries ferritic and austenitic properties together, it is called duplex stainless steel. Also they are extremely corrosion resistant, work hardenable alloys.
Duplex stainless steel solidifies from a liquid phase to a fully ferritic structure when melted. As the material cools to room temperature, about half of the ferritic grains turn into austenitic grains. As a result, duplex stainless steel is a roughly 50% austenite and 50% ferritic microstructure.
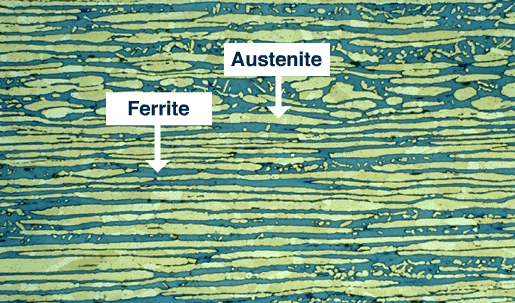
Microstructure of Duplex Steels
This combination of properties can mean some compromise when compared with pure austenitic and pure ferritic grades. Duplex stainless steel are in most cases, tougher than ferritic stainless steel. Strengths of duplex stainless steels can in some cases be double that for austenitic stainless steels.
Whilst duplex stainless steel are considered resistant to stress corrosion cracking, they are not as resistant to this form of attack as ferritic stainless steel. However, the corrosion resistance of the least resistant Duplex stainless steel is greater than that for the most commonly used grades of stainless steel, i.e. 304 and 316.
The most important feature that distinguishes this part from other ordinary stainless steels is that it is magnetic. Yes, Duplex stainless steel are also magnetic, a property that can be used to easily differentiate them from common austenitic grades of stainless.
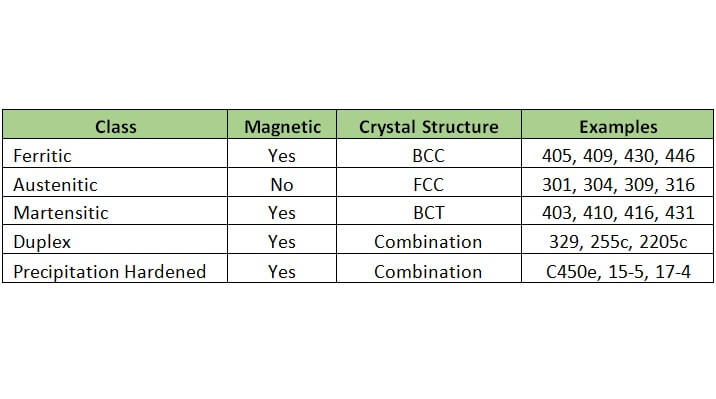
Before going into details, it is possible to list the general features as follows;
Strength: Duplex stainless steels are about twice as strong as regular austenitic or ferritic stainless steels.
Toughness and ductility: Duplex stainless steels have significantly better toughness and ductility than ferritic grades; however, they do not reach the excellent values of austenitic grades.
Corrosion resistance: As with all stainless steels, corrosion resistance depends mostly on the composition of the stainless steel. For chloride pitting and crevice corrosion resistance, their chromium, molybdenum and nitrogen content are most important. Duplex stainless steel grades have a range of corrosion resistance, similar to the range for austenitic stainless steels.
Stress corrosion cracking resistance: Duplex stainless steels show very good stress corrosion cracking (SCC) resistance, a property they have “inherited” from the ferritic side. SCC can be a problem under certain circumstances (chlorides, humidity, elevated temperature) for standard austenitics such as Types 304 and 316.
Weldability: More care should be taken than with other stainless steel derivatives. It can be welded by common types of welding, such as shielded metal arc welding, gas tungsten arc welding, plasma arc welding and submerged arc welding. When welding or making an application such as filler metal, you should use welding wires called 2205 produced in its own kind.
Cost: Duplex stainless steels have lower nickel and molybdenum contents than their austenitic counterparts of similar corrosion resistance. Due to the lower alloying content, duplex stainless steels can be lower in cost, especially in times of high alloy surcharges. Additionally, it may often be possible to reduce the section thickness of duplex stainless steel, due to its increased yield strength compared to austenitic stainless steel. The combination can lead to significant cost and weight savings compared to a solution in austenitic stainless steels.
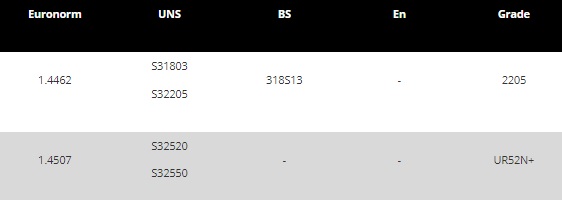
Some standard designations for duplex stainless steel alloys
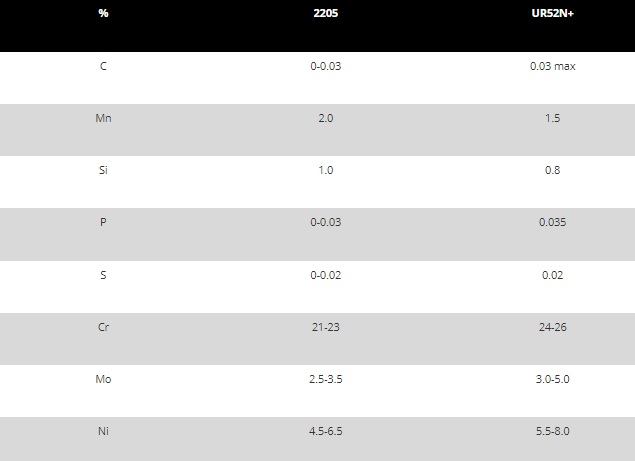
Typical chemical composition for two duplex stainless steel alloys
Note: UR52N+ contains %0.5-3 Cu.

Typical mechanical properties of two duplex stainless steel alloys
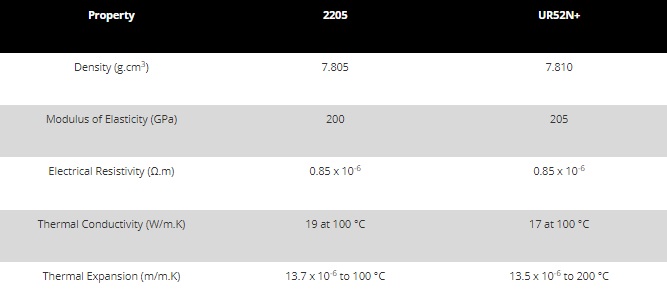
Typical physical properties of two duplex stainless steel alloys
Duplex stainless steel are extremely corrosion resistant. They have high resistance to intergranular corrosion. Even in chloride and sulphide environments, Duplex stainless steel exhibit very high resistance to stress corrosion cracking. The super duplex grades are even more resistant to corrosion.
The high chromium content of Duplex stainless steel that p rotects against corrosion, causes embrittlement at temperatures over about 300°C.
At low temperatures duplex stainless steels have better ductility than the ferritic and martensitic grades. Duplex grades can readily be used down to at least -50°C.
Fabrication of all stainless steel should be done only with tools dedicated to stainless stell materials. Tooling and work surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned before use. These precautions are necessary to avoid cross contamination of stainless steel by easily corroded metals that may discolour the surface of the fabricated product.
Duplex stainless steel cannot be hardened by heat treatment. They can however be work hardened.
Solution treatment or annealing can be done by rapid cooling after heating to around 1100°C.
Duplex stainless steel have good weldability. All standard welding processes can be used. They are not quite as easily welded as the austenitic grades but low thermal expansion in duplex grades reduces distortion and residual stresses after welding. The recommended filler material for 2205 stainless steel is 2209.
Duplex stainless steel are typically used in:
Chemical processing, transport and storage
Oil and gas exploration and offshore rigs
Oil and gas refining
Marine environments
Pollution control equipment
Pulp & paper manufacturing
Chemical process plant

Sea bridges at low altitudes are generally made of duplex stainless steel due to their good corrosion resistance.

Duplex stainless steel used in bridge construction.

Duplex stainless steel has an extremely important place in offshore structures.
Aalco typically supplies 2205 duplex stainless steel in the following forms:
Fittings & Flanges
Pipe
Plate
Sheet
Tube
Bar
And of course we have to mention the difference with its cousin “Super Duplex Stainless Steel”. Because Super Duplex is another matter; we can only summarize the difference between these two cousin materials as follows;
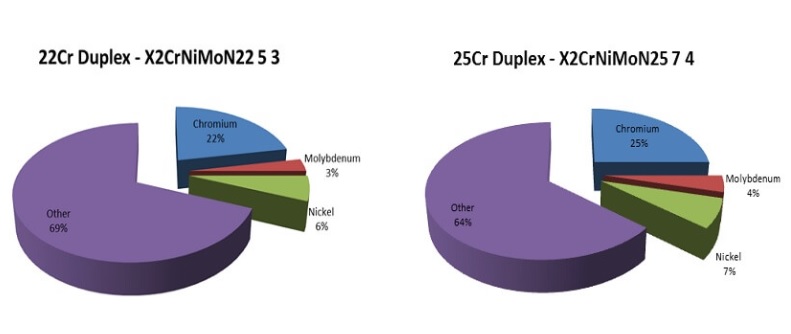
Duplex stainless steels are based on 22% chromium composition while super duplex stainless steels are based on 25% chromium composition. By increasing the chromium content, the level of pitting corrosion resistance also increases. However, it is also necessary to increase the content of nickel and other elements to maintain the proper balance of the austenitic and ferritic microstructures, increasing the cost. Hyper duplex stainless steels are currently being developed based on 27% and 29% chromium composition, but due to difficulties in forging and rolling, they are only available in tubular form, not bar or sheet yet.
As a result, duplex stainless steel’s high corrosion resistance provides significantly longer uptime than carbon steels and conventional stainless steels, while mechanical strength allows for lighter constructions, a more compact system design, and less welding.